The melting points and boiling points of some ionic compounds
Metals and Non-metals (10)The melting points and boiling points of some ionic compounds are given below:
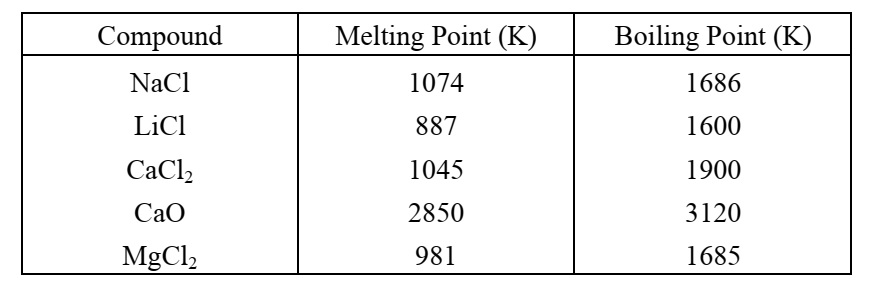
These compounds are termed ionic because they are formed by the transfer of electrons from a metal to a non-metal. The electron transfer in such compounds is controlled by the electronic configuration of the elements involved. Every element tends to attain a completely filled valence shell of its nearest noble gas or a stable octet.
- Show the electron transfer in the formation of magnesium chloride.
- List two properties of ionic compounds other than their high melting and boiling points.
- (A) While forming an ionic compound say sodium chloride how does sodium atom attain its stable configuration ?
(B) Give reasons :
i. Why do ionic compounds in the solid state not conduct electricity ?
ii. What happens at the cathode when electricity is passed through an aqueous solution of sodium chloride ?
Answer
i.
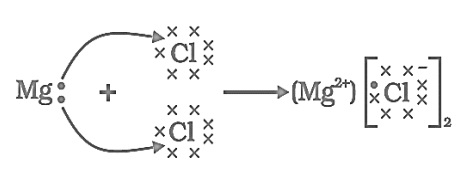
ii.
- They are hard solids
- They are soluble in water
- They conduct electricity in aqueous solution or molten state
iii.
(A) • Sodium atom has one electron in its outermost shell
• It attains its nearest noble gas configuration by losing this electron

(B).
- Because movement of ions in the solid is not possible due to their rigid structure.
- H2 gas is liberated at cathode
- Exam Year: 2023
- Why are metals good conductors of electricity whereas glass is a bad conductor of electricity
- Write the steps involved in the extraction of pure metals in the middle of the activity series
- The electron dot structure of chlorine molecule is
- Why are the heating elements of electric toasters and electric irons
- Draw a labelled diagram of the experimental set-up to study the action of steam on a metal
- Metals like sodium and potassium are stored under oil